PROS Disorders
PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Spectrum (PROS) is a spectrum of diverse overgrowth disorders caused by PIK3CA mutations1
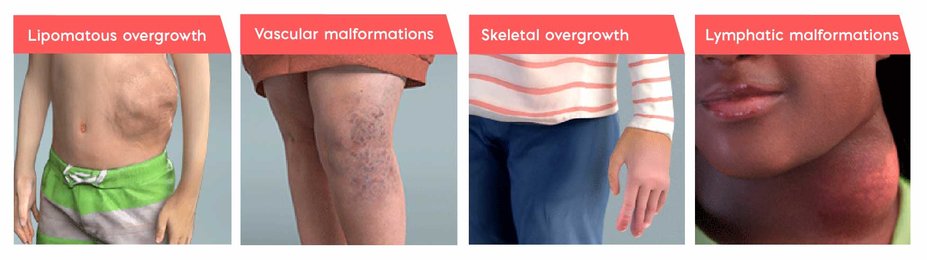
Features of PROS disorders broadly include the following types of overgrowth:
Despite the range of presentation, PROS disorders have clinical commonalities1
Clinical hallmarks of PROS include congenital or early childhood onset, sporadic and mosaic overgrowth, and a progressive course of disease.
PROS and its associated overgrowth can have a substantial effect on patients’ lives2-5
Patients with PROS experience a variety of signs and symptoms related to their disorders. These manifestations can cause severe medical complications, disfigurements, and functional complications that interfere with daily living.

Bone abnormalities, including leg asymmetry and scoliosis
Pain

Hypertrophy
Vascular complications, including disseminated intravascular coagulation
Fatigue
The effects of overgrowth can add to the already severe burden on quality of life from PROS signs and symptoms.4-7 To manage the effects of PROS, patients may require repeat surgeries, interventional procedures, and extensive care.8,9
Disorders now recognized to be part of PROS include1,10,11:
KTS (Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome)
CLOVES syndrome (Congenital Lipomatous Overgrowth, Vascular malformations, Epidermal nevi, Scoliosis/skeletal and spinal)
ILM (Isolated Lymphatic Malformation)
MCAP or M-CM (Megalencephaly-Capillary Malformation)
HME (HemiMegalEncephaly)/DMEG (Dysplastic MEGalencephaly)/Focal cortical dysplasia type II
HHML (HemiHyperplasia-Multiple Lipomatosis)
FIL (Facial Infiltrating Lipomatosis)
FAVA (FibroAdipose Vascular Anomaly)
Macrodactyly
Muscular HH (HemiHyperplasia)
FAO (FibroAdipose hyperplasia or Overgrowth)
CLAPO syndrome (Capillary malformation of the lower lip, Lymphatic malformation of the face and neck, Asymmetry of the face and limbs, and Partial or generalized Overgrowth)
Epidermal nevus, benign lichenoid keratosis, or seborrheic keratosis
+Other disorders may be identified and characterized as PROS
How VIJOICE Works
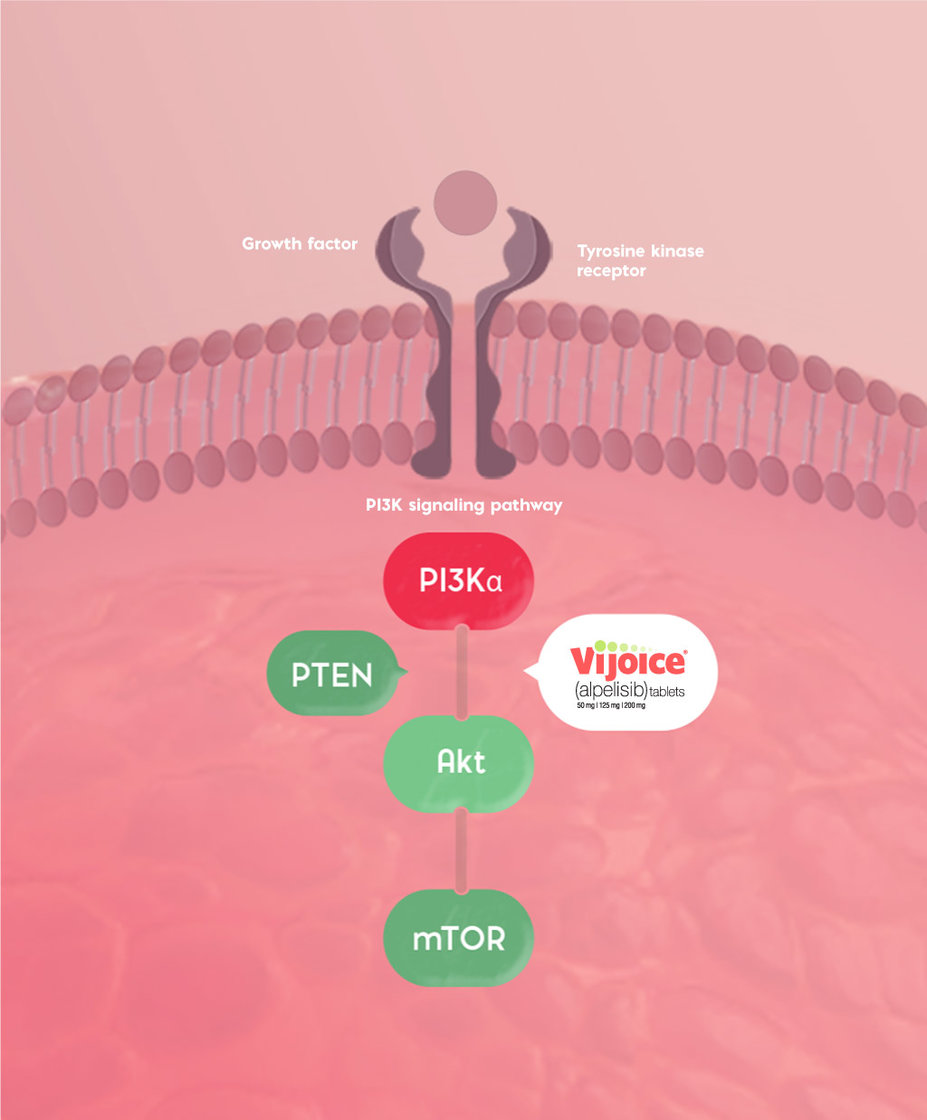
PIK3CA mutations lead to hyperactivation of PI3Kα, a key upstream component of the PI3K pathway12
The PIK3CA gene codes for the catalytic α-subunit of the PI3K protein (PI3Kα)
Mutations to this gene lead to activation of PI3Kα and Akt-signaling, cellular transformation, and the generation of tumors in in vitro and in vivo models
Inhibiting PI3K interrupts various downstream signaling, including Akt/mTOR and Akt-independent cascades12,13
In a preclinical mouse model, inhibition of PI3K with alpelisib was shown to reduce the size of overgrowth and reduce proliferation13
In an inducible mouse model of CLOVES syndrome, inhibition of the PI3K pathway with alpelisib resulted in the prevention or improvement of organ abnormalities associated with the disease, depending on when treatment with alpelisib was started. These findings were reversed after withdrawal of alpelisib12
Based on in vitro/in vivo studies.12 Preclinical activity does not necessarily correlate with clinical outcomes.
VIJOICE does not suppress the immune system13-16
VIJOICE targets the underlying cause of PROS1,17
VIJOICE is an α-selective PI3K inhibitor12
VIJOICE inhibits the α isoform of PI3K 50 times more potently than other PI3K isoforms (β, γ, δ).18
PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Akt, protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin.
Diagnosis
A PROS diagnosis is the first step to targeted treatment with VIJOICE
PROS is a spectrum of diverse overgrowth disorders caused by PIK3CA mutations.1 Understanding the diagnosis of PROS can help you identify which patients may benefit from VIJOICE, the first and only FDA-approved treatment for patients with PROS. A National Institutes of Health (NIH) workshop* proposed the following diagnostic criteria for PROS1:
NIH Workshop Diagnostic Criteria1,*

Congenital or early childhood onset

Sporadic and mosaic overgrowth

2 or more spectrum features OR any 1 isolated feature
Spectrum features (2 or more)
Overgrowth: adipose, muscle, nerve, skeletal
Epidermal nevus
Vascular malformations: capillary, venous, arteriovenous, lymphatic
Isolated features (any 1)
Large, isolated lymphatic malformation
Truncal adipose overgrowth
Benign lichenoid keratoses
Seborrheic keratoses
HME (bilateral)/DMEG/focal cortical dysplasia type II
Isolated macrodactyly or overgrown, splayed feet/hands, overgrown limbs
Epidermal nevus

Presence of a somatic PIK3CA mutation
Due to the mosaic nature of PIK3CA mutations in PROS, genomic testing may not always reveal the presence of a PIK3CA mutation1
Detection of a PIK3CA mutation depends on the degree of overgrowth, as well as the distribution and amount of detectable mutation in the tissue1
Technical limitations, sample availability, and difficulties with interpreting the results may impact the decision to test1,19,20
A presumptive PROS diagnosis can be considered based on features if a PIK3CA mutation is not identified1,19,20
*Clinical diagnostic criteria were determined after a 2-day workshop that included several researchers who have been studying this group of disorders and 3 parent representatives of patient-family support and advocacy organizations for individuals with these conditions. These criteria may change as research develops.1
Find a multidisciplinary team
The International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies (ISSVA) has compiled a list of multidisciplinary teams that treat vascular anomalies, which may be a manifestation of PROS. ISSVA believes "that a team environment is the optimal setting for managing the complex problems that arise in treating vascular anomalies."
To view the list of multidisciplinary care teams, click here ↗.